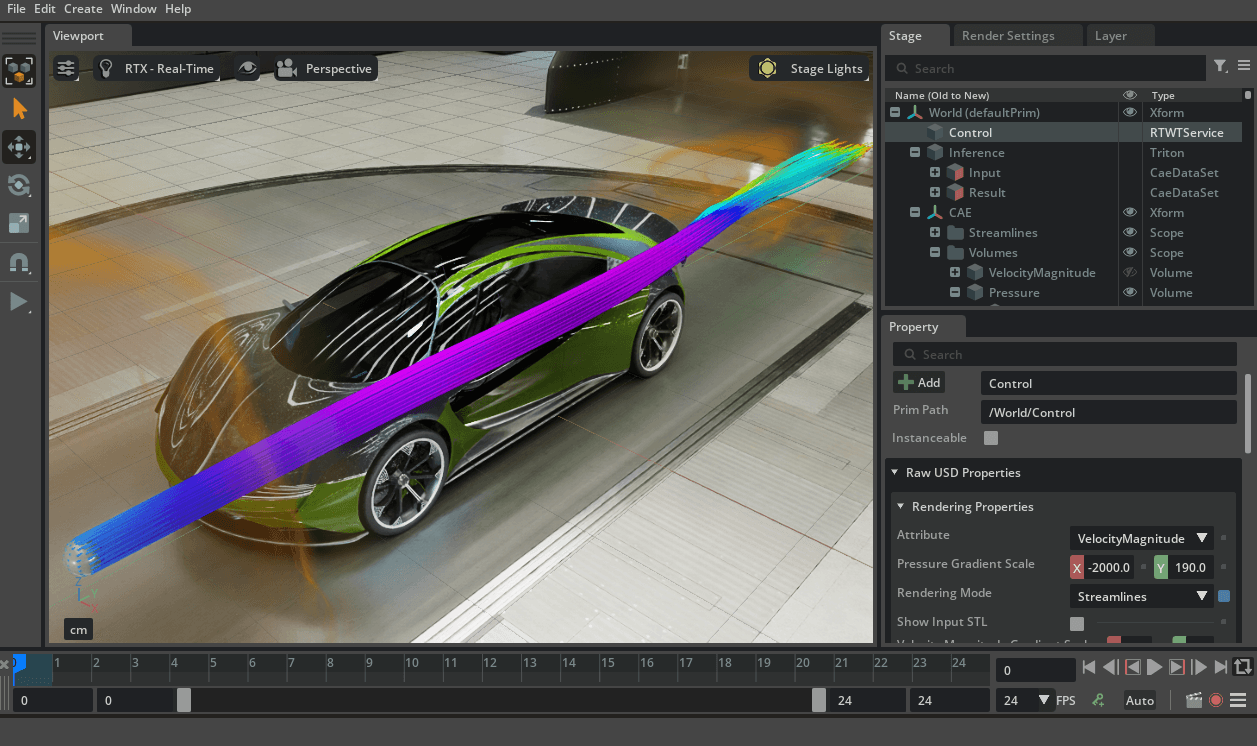
Kit-CAE is a sample application on the NVIDIA Omniverse platform that demonstrates workflows for processing and rendering CAE (Computer-Aided Engineering) data.
Main Objectives of the Project
Core Structure
1. USD Schemas (usdSchema/)
2. Key Extensions
Data Processing Core:
omni.cae.data: Provides the Data Delegate APIomni.cae.algorithms.core: Manages algorithm executionFile Format Support:
omni.cae.cgns: CGNS file supportomni.cae.npz: NumPy file supportomni.cae.vtk: VTK file supportomni.cae.ensight: EnSight file supportData Importers:
omni.cae.asset_importer.*: Import various file formats into a USD stageAdvanced Processing:
omni.cae.index: Volume rendering with IndeXomni.cae.flow: Flow-based fluid simulationomni.cae.algorithms.warp: NVIDIA Warp-based algorithmsBuild Steps Executed
./repo.sh schema: Build USD schemasusdSchema/./repo.sh build -r: Build Omniverse extensions./repo.sh launch -n omni.cae.kit: Launch the applicationAdditional Features
Run the VTK-enabled variant:
./repo.sh launch -n omni.cae_vtk.kit
Run a sample script:
./repo.sh launch -n omni.cae.kit -- --exec scripts/example-bounding-box.py
Supported Data Formats
This project provides a complete framework for efficiently processing and visualizing scientific simulation data within the Omniverse ecosystem.
Prerequisites
sudo apt install git-lfs
git lfs install
git lfs pull
mkdir -p pip_archives
./repo.sh pip_download --dest pip_archives -r ./tools/deps/requirements.txt
| # | Example | Application | Data Source | Key Function | Physical Background | Research Use |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Geometric Analysis | ||||||
| 1 | example-bounding-box.py | omni.cae.kit | StaticMixer.cgns | Extract AABB bounding boxes | Compute grid domain extents | Domain size validation, grid quality checks |
| 2 | example-faces.py | omni.cae.kit | StaticMixer.cgns | Extract external surfaces | Volume→surface topology conversion | Wall BC visualization, surface roughness analysis |
| 3 | example-points.py | omni.cae.kit | StaticMixer.cgns | Point-cloud view | Scalar mapping on grid nodes | Grid uniformity, temperature gradient analysis |
| 4 | example-glyphs.py | omni.cae.kit | StaticMixer.cgns | Vector field arrows | 3-component velocity glyphs | Flow pattern analysis, vortex structure ID |
| Advanced Rendering (IndeX) | ||||||
| 5 | example-slice.py | omni.cae.kit | StaticMixer.cgns | 2D slice rendering | GPU volume slicing | Turbulence structure, mixing-layer thickness |
| 6 | example-volume.py | omni.cae.kit | StaticMixer.cgns | 3D volume rendering | Ray-march transparency | 3D turbulence, vortex core identification |
| By Data Type | ||||||
| 7 | example-npz.py | omni.cae.kit | disk_out_ref.npz | NPZ streamlines | Lagrangian particle tracking | Rotating body aero/thermal paths |
| 8 | example-npz-point-cloud.py | omni.cae.kit | disk_out_ref.npz | NanoVDB volume from points | Point→volume voxelization | Particle sims, sparse data viz |
| VTK-based | ||||||
| 9 | example-headsq-vti.py | omni.cae_vtk.kit | headsq.vti | VTI→NanoVDB + ROI | Structured medical grids | CT/MRI analysis, ROI focus |
| 10 | example-streamlines.py | omni.cae_vtk.kit | StaticMixer.cgns | High-precision streamlines | RK4/RK45 integrators | Precision flow analysis, mixing efficiency |
| Flow/NanoVDB Advanced | ||||||
| 11 | example-npz-volume-streamlines.py | omni.cae.kit | disk_out_ref.npz | Flow-based dynamic streamlines | Real-time volume streamlines | Dynamic flow, particle tracking |
| 12 | example-nvdb-slice.py | omni.cae.kit | StaticMixer.cgns | NanoVDB slice | GPU-efficient slicing | Large-data slicing |
| 13 | example-nvdb-slice-on-volume.py | omni.cae.kit | StaticMixer.cgns | Slice over NanoVDB volume | Resolution-capped perf | Perf/quality balancing |
| 14 | example-slice-on-volume.py | omni.cae.kit | StaticMixer.cgns | IndeX volume-based slice | Colormap inheritance | Consistent visualization settings |
Categorized by Tech Stack
| Tech | # of Examples | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| NVIDIA IndeX | 6 | slice, volume, nvdb-slice, slice-on-volume, nvdb-slice-on-volume, headsq-vti |
| NanoVDB | 4 | npz-point-cloud, headsq-vti, nvdb-slice, nvdb-slice-on-volume |
| VTK | 2 | headsq-vti, streamlines |
| Flow | 1 | npz-volume-streamlines |
| CGNS | 10 | Most StaticMixer.cgns examples |
| NumPy | 3 | npz, npz-point-cloud, npz-volume-streamlines |
Command Summary
Core Examples (12)
./repo.sh launch -n omni.cae.kit -- --exec scripts/[예제명].py
VTK Examples (2)
# VTK 설정 (최초 1회)
mkdir -p pip_archives
./repo.sh pip_download --dest pip_archives -r ./tools/deps/requirements.txt
# 실행
./repo.sh launch -n omni.cae_vtk.kit -- --/exts/omni.kit.pipapi/archiveDirs=[pip_archives] --exec scripts/[예제명].py
This document systematically analyzes all Kit-CAE example scripts and summarizes their outputs.
Kit-CAE provides 14 example scripts, categorized as follows:
Supported by the core Kit-CAE app (omni.cae.kit, 12 examples)
Requires the VTK build (omni.cae_vtk.kit, 2 examples)
By Advanced Feature
Runnable with the core Kit-CAE (omni.cae.kit):
✅ example-bounding-box.py
✅ example-faces.py
✅ example-glyphs.py
✅ example-points.py
✅ example-npz.py
✅ example-slice.py
✅ example-volume.py
✅ example-npz-point-cloud.py
Requires the VTK variant (omni.cae_vtk.kit):
✅ example-headsq-vti.py (VTK 임포터 필요)
✅ example-streamlines.py (VTK 스트림라인)
Flow/NanoVDB advanced examples:
✅ example-npz-volume-streamlines.py (Flow 기반 볼륨 스트림라인)
✅ example-nvdb-slice.py (NanoVDB 슬라이스)
✅ example-nvdb-slice-on-volume.py (NanoVDB 볼륨 슬라이스)
✅ example-slice-on-volume.py (IndeX 볼륨 슬라이스)
1. example-bounding-box.py
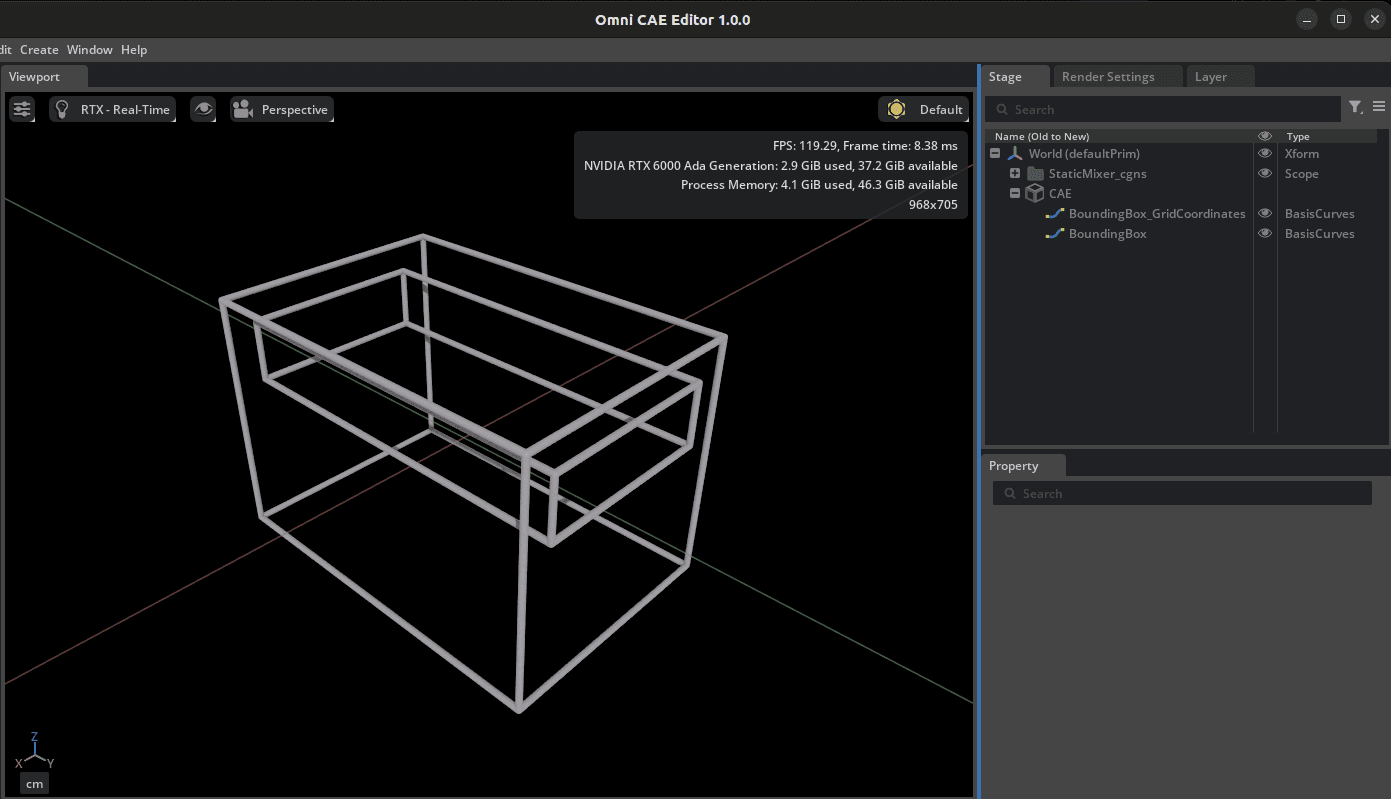
Run:
./repo.sh launch -n omni.cae.kit -- --exec scripts/example-bounding-box.py
Analysis:
Physical Context:
Key Code:
# 1) Single-dataset bounding box (whole domain)
dataset_path = "/World/StaticMixer_cgns/Base/StaticMixer/GridCoordinates"
viz_path = "/World/CAE/BoundingBox_GridCoordinates"
omni.kit.commands.execute("CreateCaeAlgorithmsExtractBoundingBox",
dataset_paths=[dataset_path], prim_path=viz_path)
# 2) Combined bounding box for multiple datasets (inlets)
dataset_paths = [
"/World/StaticMixer_cgns/Base/StaticMixer/in1",
"/World/StaticMixer_cgns/Base/StaticMixer/in2"
]
viz_path2 = "/World/CAE/BoundingBox_Inlets"
omni.kit.commands.execute("CreateCaeAlgorithmsExtractBoundingBox",
dataset_paths=dataset_paths, prim_path=viz_path2)
# 3) Auto frame the camera (whole domain)
omni.kit.commands.execute("FrameSelection", prim_paths=[viz_path], zoom=0.8)
Technical Highlights:
Research Uses: Domain size validation, grid quality checks, BC location verification, spatial relationships across multi-physics regions
2. example-faces.py
Run:
./repo.sh launch -n omni.cae.kit -- --exec scripts/example-faces.py
Analysis:
Key Code:
dataset_path = "/World/StaticMixer_cgns/Base/StaticMixer/B1_P3"
viz_path = "/World/CAE/ExternalFaces_B1_P3"
omni.kit.commands.execute("CreateCaeAlgorithmsExtractExternalFaces",
dataset_path=dataset_path, prim_path=viz_path)
omni.kit.commands.execute("FrameSelection", prim_paths=[viz_path], zoom=0.05)
Technical Highlights:
Research Uses: Wall-BC visualization, surface roughness, heat-transfer area, pressure mapping, shape-optimization checks
3. example-points.py
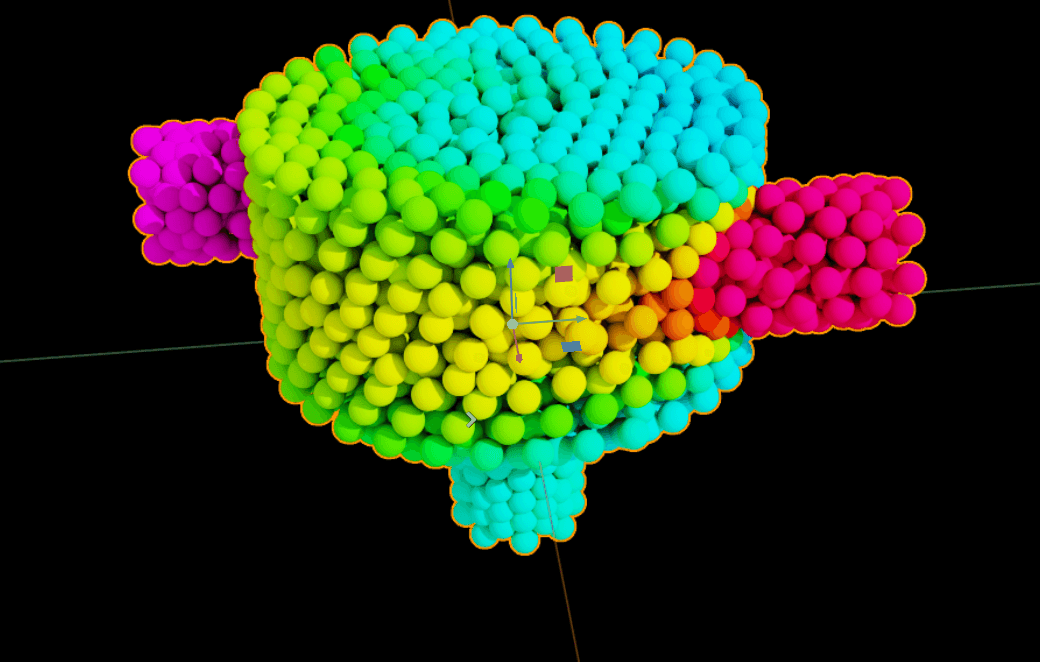
Run:
./repo.sh launch -n omni.cae.kit -- --exec scripts/example-points.py
Analysis:
Key Code:
dataset_path = "/World/StaticMixer_cgns/Base/StaticMixer/GridCoordinates"
viz_path = "/World/CAE/Points_GridCoordinates"
omni.kit.commands.execute("CreateCaeAlgorithmsExtractPoints",
dataset_path=dataset_path, prim_path=viz_path)
viz_prim = stage.GetPrimAtPath(viz_path)
viz_prim.GetAttribute("omni:cae:algorithms:points:width").Set(0.25)
viz_prim.GetRelationship("omni:cae:algorithms:points:colors").SetTargets(
["/World/StaticMixer_cgns/Base/StaticMixer/Flow_Solution/Temperature"]
)
omni.kit.commands.execute("FrameSelection", prim_paths=[viz_path])
Technical Highlights:
Research Uses: Grid quality (uniformity), temperature gradients, adaptivity checks, numerical diffusion patterns, convergence studies
4. example-glyphs.py
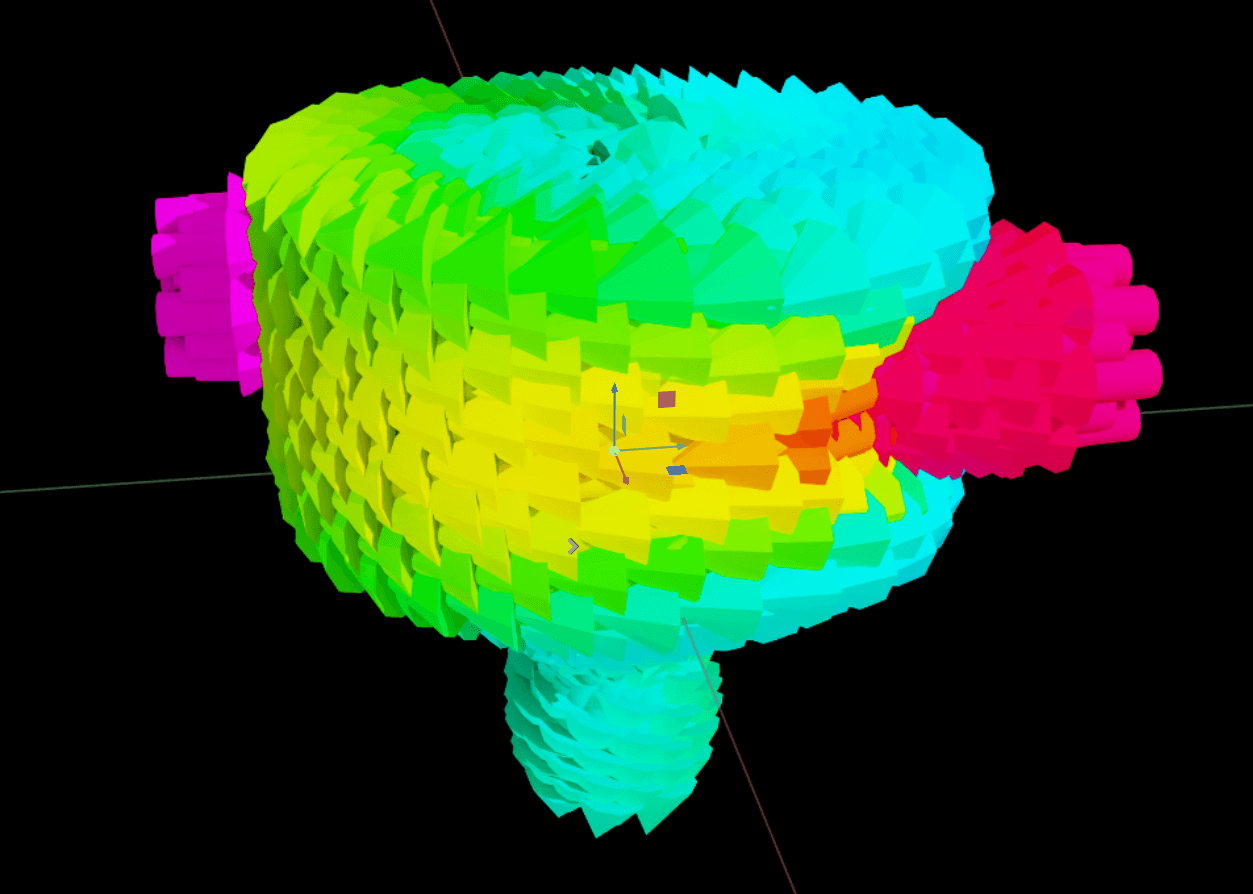
Run:
./repo.sh launch -n omni.cae.kit -- --exec scripts/example-glyphs.py
Analysis:
Physical Context:
Key Code:
dataset_path = "/World/StaticMixer_cgns/Base/StaticMixer/B1_P3"
viz_path = "/World/CAE/Glpyhs_B1_P3"
omni.kit.commands.execute("CreateCaeAlgorithmsGlyphs",
dataset_path=dataset_path, prim_path=viz_path)
arrow_path = viz_path + "/Protos/ArrowXform"
arrow_prim = stage.GetPrimAtPath(arrow_path)
UsdGeom.XformCommonAPI(arrow_prim).SetScale((0.1, 0.1, 0.1))
viz_prim.GetRelationship("omni:cae:algorithms:glyphs:orientation").SetTargets([
"/World/StaticMixer_cgns/Base/StaticMixer/Flow_Solution/VelocityX",
"/World/StaticMixer_cgns/Base/StaticMixer/Flow_Solution/VelocityY",
"/World/StaticMixer_cgns/Base/StaticMixer/Flow_Solution/VelocityZ"
])
viz_prim.GetRelationship("omni:cae:algorithms:glyphs:colors").SetTargets(
["/World/StaticMixer_cgns/Base/StaticMixer/Flow_Solution/Temperature"]
)
Technical Highlights:
Research Uses: Velocity–temperature correlation, mixing efficiency, heat-transfer visualization, vortex ID
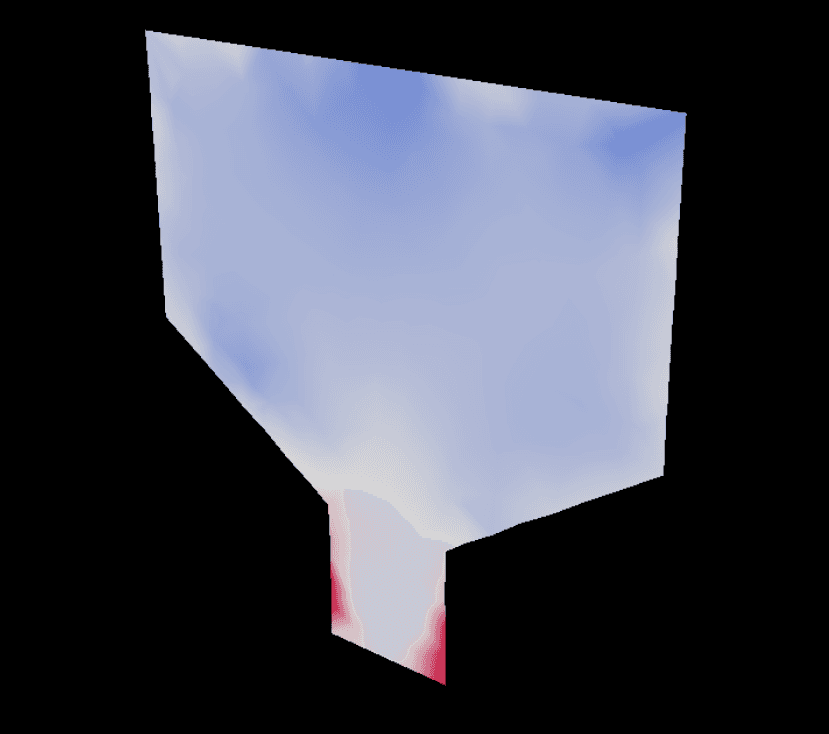
5. example-slice.py
실Run:
./repo.sh launch -n omni.cae.kit -- --exec scripts/example-slice.py
Analysis:
Key Code:
dataset_path = "/World/StaticMixer_cgns/Base/StaticMixer/B1_P3"
slice_path = "/World/CAE/IndeXSlice_B1_P3"
omni.kit.commands.execute("CreateCaeIndeXSlice",
dataset_path=dataset_path, prim_path=slice_path)
slice_prim = stage.GetPrimAtPath(slice_path)
slice_prim.GetRelationship("omni:cae:index:slice:field").SetTargets(
["/World/StaticMixer_cgns/Base/StaticMixer/Flow_Solution/Eddy_Viscosity"]
)
for i in range(10):
await asyncio.sleep(0.1)
await omni.kit.app.get_app().next_update_async()
Technical Highlights: GPU acceleration, adaptive sampling, live colormaps, memory efficiency
Research Uses: Turbulence structure, mixing layer, shear stress, separation zones, turbulence-model validation
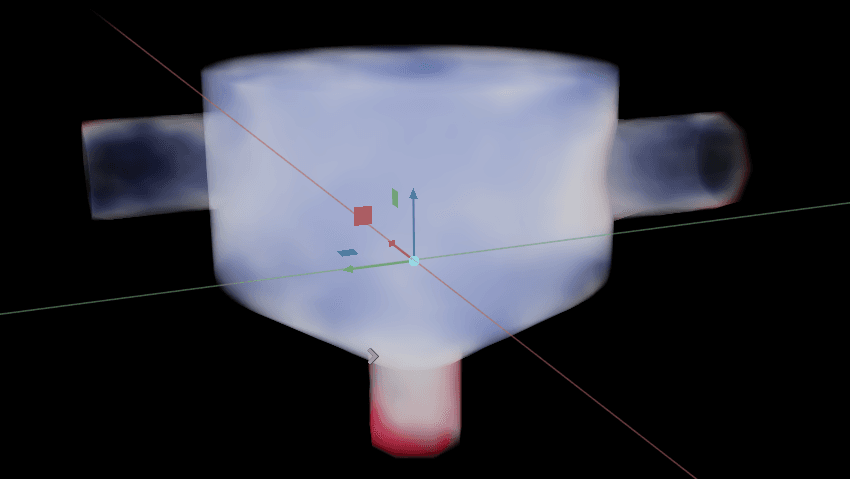
6. example-volume.py
Run:
./repo.sh launch -n omni.cae.kit -- --exec scripts/example-volume.py
Analysis:
Physical Context: Volume rendering, transfer functions, ray-marching, μₜ distribution
Key Code:
dataset_path = "/World/StaticMixer_cgns/Base/StaticMixer/B1_P3"
viz_path = "/World/CAE/IndeXVolume_B1_P3"
omni.kit.commands.execute("CreateCaeIndeXVolume",
dataset_path=dataset_path, prim_path=viz_path)
viz_prim = stage.GetPrimAtPath(viz_path)
viz_prim.GetRelationship("omni:cae:index:volume:field").SetTargets(
["/World/StaticMixer_cgns/Base/StaticMixer/Flow_Solution/Eddy_Viscosity"]
)
omni.kit.commands.execute("FrameSelection", prim_paths=[viz_path])
Technical Highlights: Ray casting, adaptive sampling, transfer-function tuning, LOD
Research Uses: 3D turbulence structure, vortex cores, mixing quantification, volumetric patterns
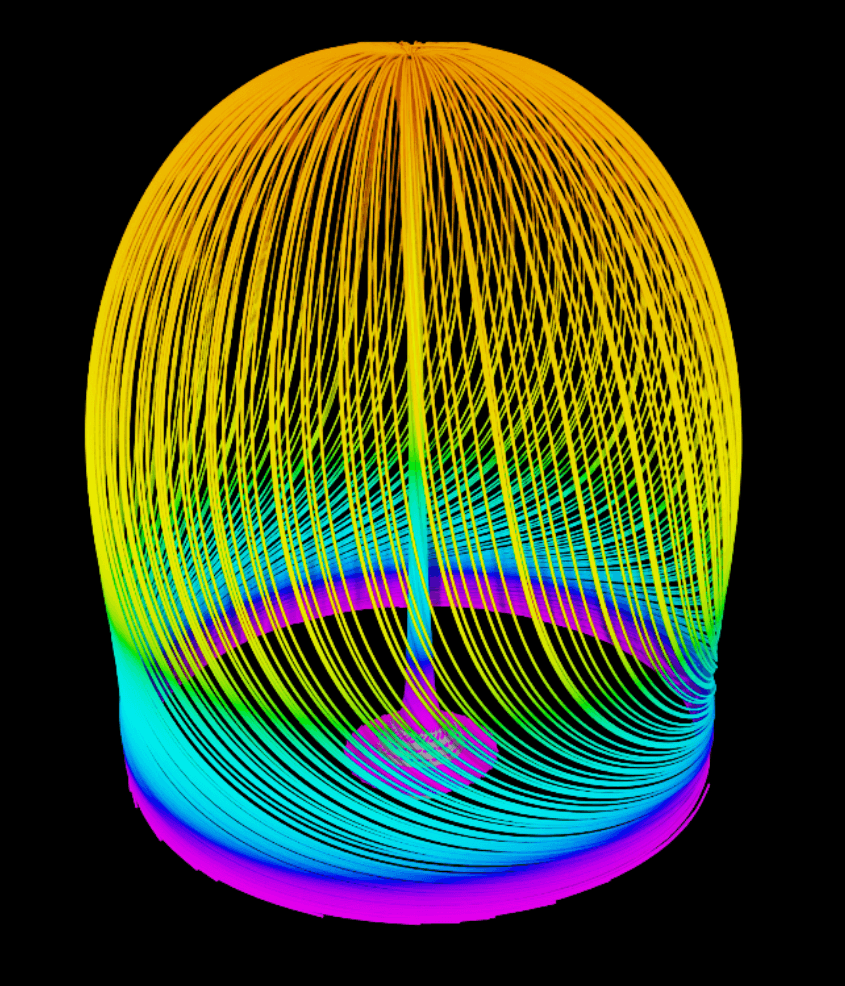
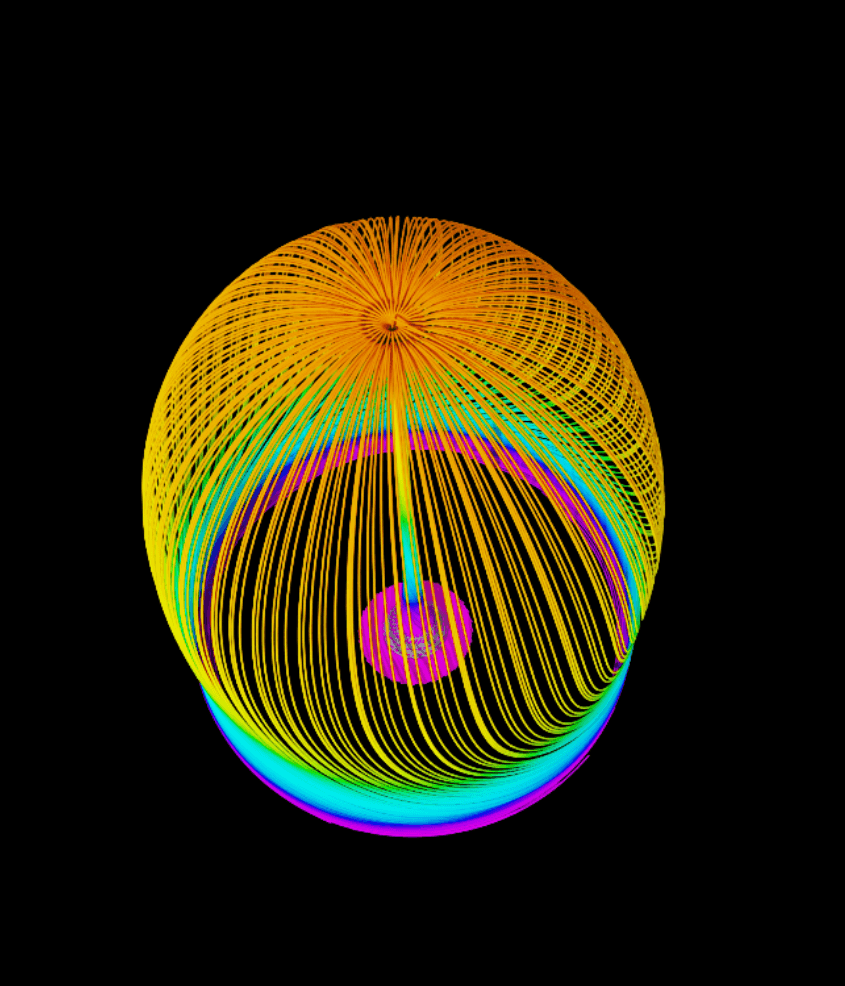
7. example-npz.py
Run:
./repo.sh launch -n omni.cae_vtk.kit -- --/exts/omni.kit.pipapi/archiveDirs=[pip_archives] --exec scripts/example-npz.py
Analysis:
Physical Context: NPZ arrays, SIDS Unstructured mapping, streamlines, Lagrangian tracking
Key Code:
# 1. NPZ 파일을 USD 스키마로 변환
async def npz_to_usd(npz_path: str, mesh_schema_type):
importer = NPZAssetImporter()
importer._options_builder.get_import_context().mesh_schema_type = mesh_schema_type
out = await importer.convert_assets([npz_path], import_as_reference=True)
return next(iter(out.values()))
usd_path = await npz_to_usd(npz_path=npz_path, mesh_schema_type="SIDS Unstructured")
# 2. 필드 연관성 설정 (vertex-centered 데이터)
array_paths = ["/World/disk_out_ref_npz/NumPyArrays/V",
"/World/disk_out_ref_npz/NumPyArrays/Temp"]
for array_path in array_paths:
array_prim = stage.GetPrimAtPath(array_path)
array_prim.GetAttribute("fieldAssociation").Set("vertex")
# 3. 스트림라인 알고리즘 생성
dataset_path = "/World/disk_out_ref_npz"
viz_path = "/World/CAE/Streamlines_disk_out_ref_npz"
omni.kit.commands.execute("CreateCaeStreamlines",
dataset_path=dataset_path, prim_path=viz_path)
# 4. 구형 시드 영역 설정
sphere_path = "/World/CAE/StreamlineSeed"
omni.kit.commands.execute("CreateMeshPrim", prim_type="Sphere", prim_path=sphere_path)
UsdGeom.XformCommonAPI(sphere_prim).SetScale((0.01, 0.01, 0.01))
# 5. 속도 벡터 및 색상 매핑
viz_prim.GetRelationship("omni:cae:algorithms:streamlines:seeds").SetTargets([sphere_path])
viz_prim.GetRelationship("omni:cae:algorithms:streamlines:velocity").SetTargets(
["/World/disk_out_ref_npz/NumPyArrays/V"]
)
viz_prim.GetRelationship("omni:cae:algorithms:streamlines:colors").SetTargets(
["/World/disk_out_ref_npz/NumPyArrays/Temp"]
)
Technical Highlights: NumPy→SIDS→USD conversion, RK4 integration, spherical seeding, color interpolation
Research Uses: Rotating machinery, heat-transfer paths, Python simulation validation, qualitative flow analysis
8. example-npz-point-cloud.py
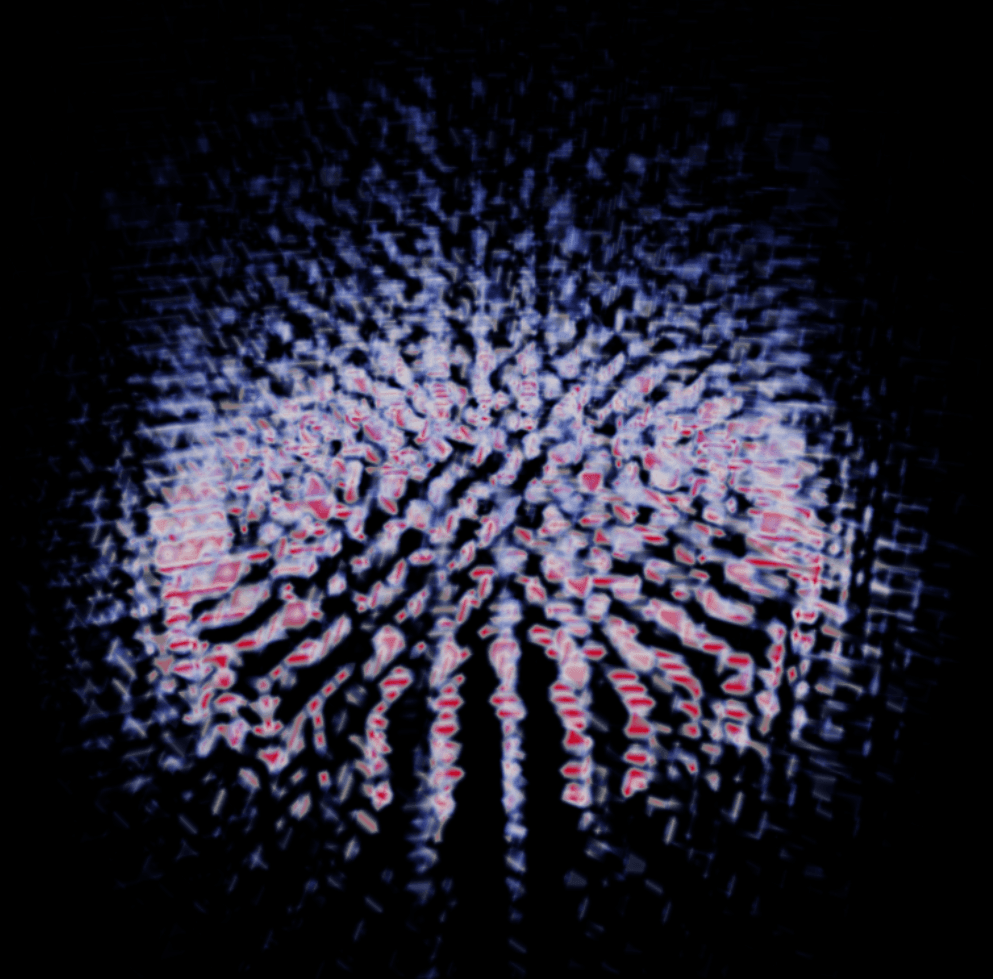
Run:
./repo.sh launch -n omni.cae.kit -- --exec scripts/example-npz-point-cloud.py
Analysis:
Physical Context: Point clouds, NanoVDB, voxelization (Gaussian splatting), temperature field
Key Code:
async def npz_to_usd(npz_path: str, mesh_schema_type):
importer = NPZAssetImporter()
importer._options_builder.get_import_context().mesh_schema_type = mesh_schema_type
out = await importer.convert_assets([npz_path], import_as_reference=True)
return next(iter(out.values()))
usd_path = await npz_to_usd(npz_path=npz_path, mesh_schema_type="Point Cloud")
dataset_path = "/World/disk_out_ref_npz"
viz_path = "/World/CAE/NanoVdbIndeXVolume_disk_out_ref_npz"
omni.kit.commands.execute("CreateCaeNanoVdbIndeXVolume",
dataset_path=dataset_path, prim_path=viz_path)
viz_prim = stage.GetPrimAtPath(viz_path)
viz_prim.GetRelationship("omni:cae:index:nvdb:field").SetTargets(
["/World/disk_out_ref_npz/NumPyArrays/Temp"])
colormap_prim = stage.GetPrimAtPath(viz_path + "/Material/Colormap")
colormap_prim.GetAttribute("domain").Set(Gf.Vec2f(0.0, 100.0))
Technical Highlights: Gaussian splatting, sparse volumes, GPU voxelization, adaptive resolution
Research Uses: Lagrangian particle analyses, sparse measurement viz, MD post-processing, reconstructing continuous fields
Note: The following require VTK and must run under omni.cae_vtk.kit.
Verify VTK Setup
ls -la pip_archives/
# Expect: vtk-9.4.0-...whl (~105MB)
9. example-headsq-vti.py (Requires VTK)
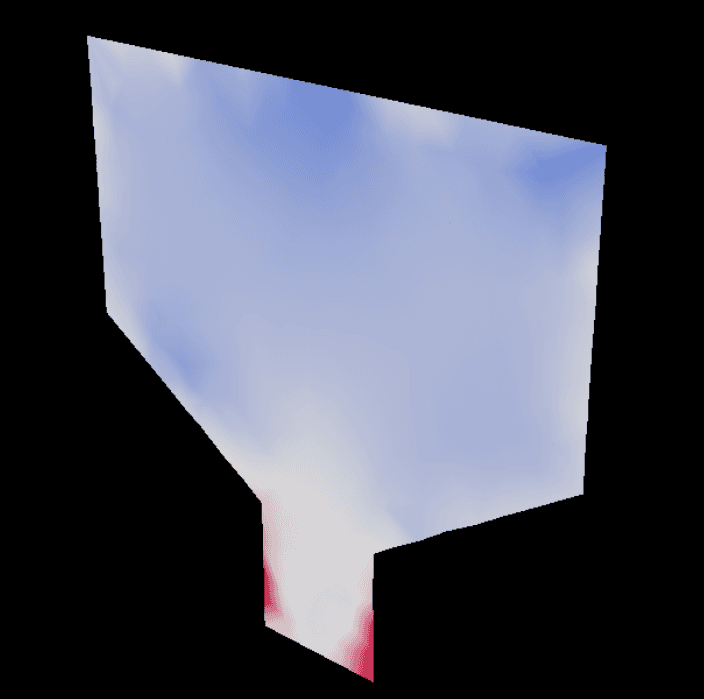
![./repo.sh launch -n omni.cae_vtk.kit -- --/exts/omni.kit.pipapi/archiveDirs=[pip_archives] --exec scripts/example-headsq-vti.py](/_next/image?url=https%3A%2F%2Fcdn.sanity.io%2Fimages%2F2b65j0c7%2Fpollux-live%2F58cdf8f1f98a55a16b97376b35d4892fe42130b8-581x459.png&w=3840&q=75)
Run:
# First-time VTK package download
mkdir -p pip_archives
./repo.sh pip_download --dest pip_archives -r ./tools/deps/requirements.txt
# Launch VTK-enabled app
./repo.sh launch -n omni.cae_vtk.kit -- --/exts/omni.kit.pipapi/archiveDirs=[pip_archives] --exec scripts/example-headsq-vti.py
Analysis:
Physical Context: VTI (VTK ImageData), CT/MRI intensity, ROI selection, structured grids
Key Code:
async def vti_to_usd(vti_path: str):
importer = VTKImporter()
out = await importer.convert_assets([vti_path], import_as_reference=True)
return next(iter(out.values()))
usd_path = await vti_to_usd(vti_path=vti_path)
dataset_path = "/World/headsq_vti"
viz_path = "/World/CAE/NanoVdbIndeXVolume_headsq_vti"
omni.kit.commands.execute("CreateCaeNanoVdbIndeXVolume",
dataset_path=dataset_path, prim_path=viz_path)
viz_prim = stage.GetPrimAtPath(viz_path)
viz_prim.GetRelationship("omni:cae:index:nvdb:field").SetTargets(
["/World/headsq_vti/PointData/Scalars_"])
bbox_path = "/World/CAE/BoundingBox_headsq_vti"
omni.kit.commands.execute("CreateCaeAlgorithmsExtractBoundingBox",
dataset_paths=[dataset_path], prim_path=bbox_path)
UsdGeom.XformCommonAPI(stage.GetPrimAtPath(bbox_path)).SetScale((0.5, 1.0, 1.0))
viz_prim.GetRelationship("omni:cae:index:nvdb:roi").SetTargets([bbox_path])
Technical Highlights: Structured-grid handling, ROI clipping, medical transfer functions, memory efficiency
Research Uses: CT/MRI diagnostics, bio-tissue modeling, structured-grid CFD, ROI-focused analysis
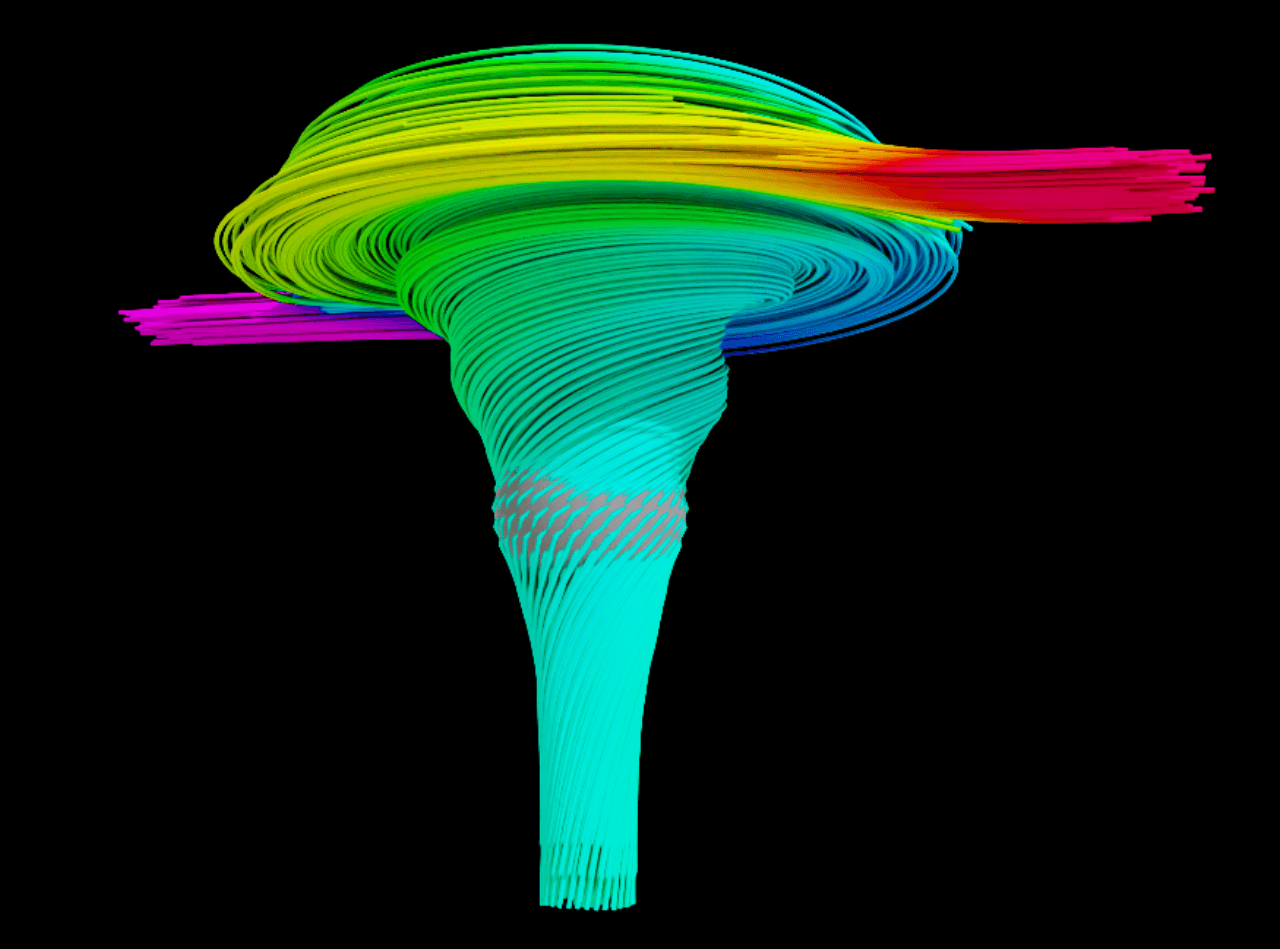
10. example-streamlines.py (Requires VTK)

Run:
./repo.sh launch -n omni.cae_vtk.kit -- --/exts/omni.kit.pipapi/archiveDirs=[pip_archives] --exec scripts/example-streamlines.py
Analysis:
Physical Context: VTK streamlines (RK4/RK45), adaptive step sizes, high-precision interpolation, smooth streamlines
Key Code:
dataset_path = "/World/StaticMixer_cgns/Base/StaticMixer/B1_P3"
viz_path = "/World/CAE/Streamlines_B1_P3"
omni.kit.commands.execute("CreateCaeStreamlines",
dataset_path=dataset_path, prim_path=viz_path)
sphere_path = "/World/CAE/StreamlineSeed"
omni.kit.commands.execute("CreateMeshPrim", prim_type="Sphere", prim_path=sphere_path)
UsdGeom.XformCommonAPI(stage.GetPrimAtPath(sphere_path)).SetScale((0.01, 0.01, 0.01))
viz_prim = stage.GetPrimAtPath(viz_path)
viz_prim.GetRelationship("omni:cae:algorithms:streamlines:seeds").SetTargets([sphere_path])
flow = "/World/StaticMixer_cgns/Base/StaticMixer/Flow_Solution"
viz_prim.GetRelationship("omni:cae:algorithms:streamlines:velocity").SetTargets(
[f"{flow}/VelocityX", f"{flow}/VelocityY", f"{flow}/VelocityZ"])
viz_prim.GetRelationship("omni:cae:algorithms:streamlines:colors").SetTargets(
[f"{flow}/Temperature"])
Technical Highlights: RK4/5 integrators, adaptive steps, precise cell-point interpolation, smooth curves
Research Uses: Precision CFD, vortex quantification, mixing efficiency, turbomachinery validation, turbulence statistics
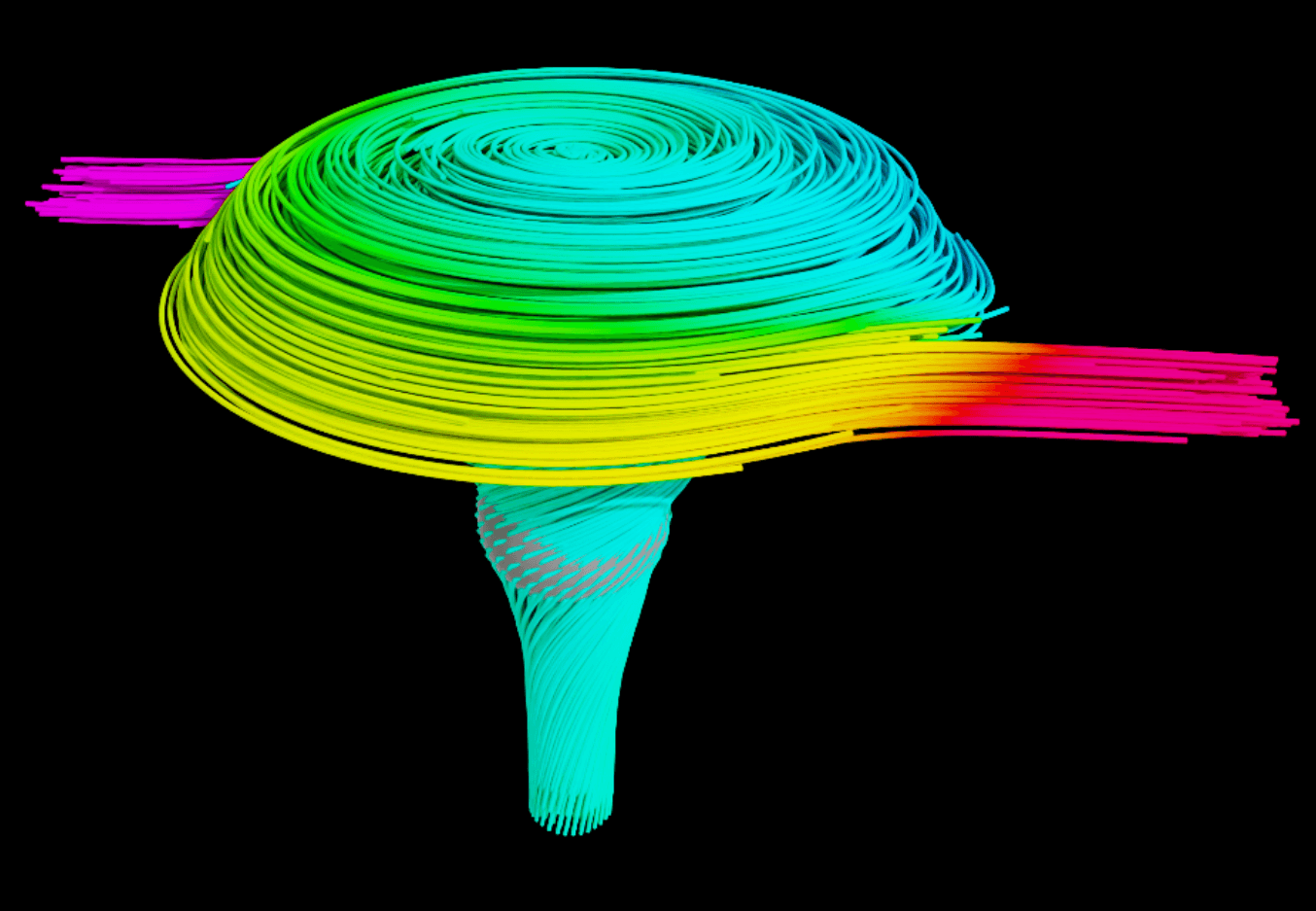
11. example-npz-volume-streamlines.py
Run:
./repo.sh launch -n omni.cae.kit -- --exec scripts/example-npz-volume-streamlines.py
Analysis:
Features:
CreateCaeFlowEnvironment + CreateCaeFlowSmokerCreateCaeFlowDataSetEmitterV and set velocityScale=2.0Use Cases: Dynamic flow visualization, real-time particle tracking, volume-based flow analysis
Code Notes (Path Wiring):
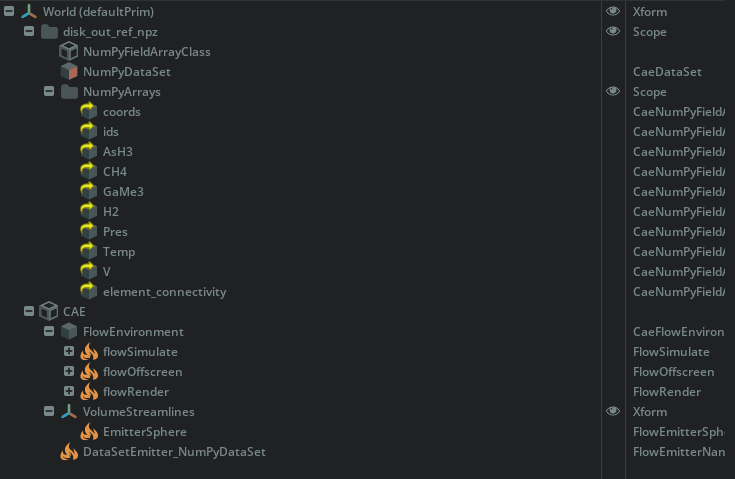
# Step 1: Field association → vertex
array_base_path = "/World/disk_out_ref_npz/NumPyArrays"
for name in ["AsH3", "CH4", "GaMe3", "H2", "Pres", "Temp", "V"]:
stage.GetPrimAtPath(f"{array_base_path}/{name}").GetAttribute("fieldAssociation").Set("vertex")
# Step 2: Flow dataset and velocity targets
dataset_path = "/World/disk_out_ref_npz/NumPyDataSet"
velocity_target = "/World/disk_out_ref_npz/NumPyArrays/V"
12. example-nvdb-slice.py

Run:
./repo.sh launch -n omni.cae.kit -- --exec scripts/example-nvdb-slice.py
Analysis:
CreateCaeIndeXNanoVdbSlice, Eddy_Viscosity NVDB field, memory-efficient processing, async stage updatesUse Cases: Efficient slicing of large data, real-time cross-sections, GPU memory optimization
13. example-nvdb-slice-on-volume.py
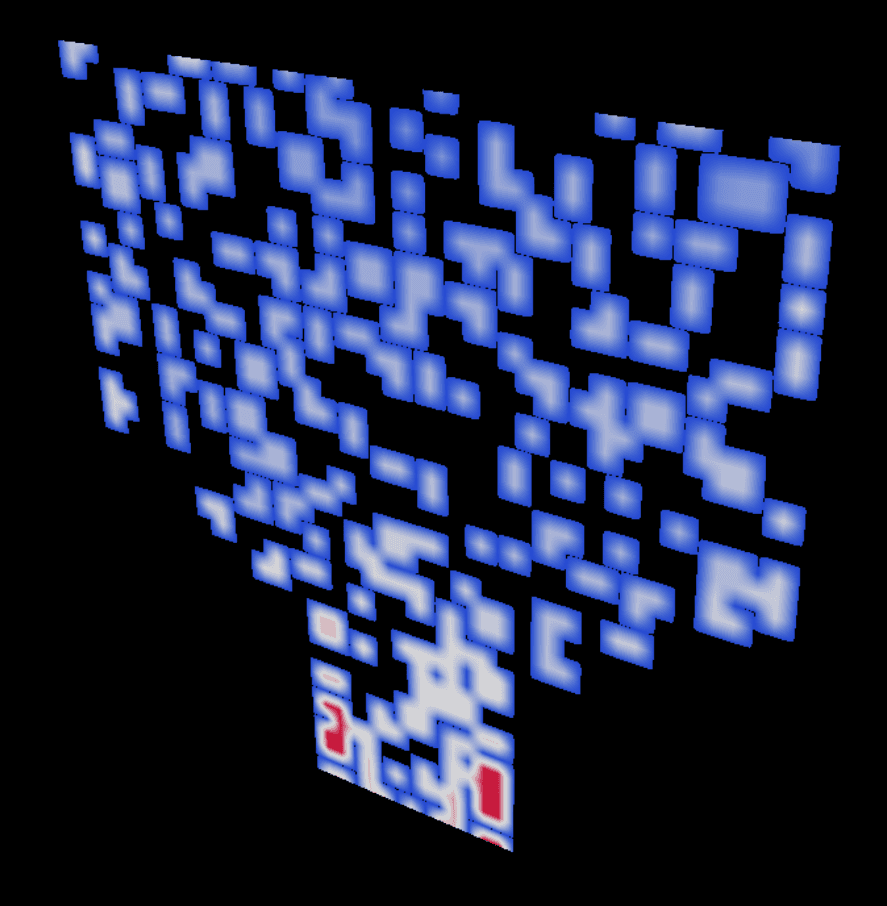
Run:
./repo.sh launch -n omni.cae.kit -- --exec scripts/example-nvdb-slice-on-volume.py
Analysis:
CreateCaeNanoVdbIndeXVolume (hidden base), CreateCaeIndeXVolumeSlice, Eddy_Viscosity mapping, maxResolution=64 perf capUse Cases: Selective visualization, perf/quality tuning, composite workflows
14. example-slice-on-volume.py
Run:
./repo.sh launch -n omni.cae.kit -- --exec scripts/example-slice-on-volume.py
Analysis:
CreateCaeIndeXVolume (hidden base), CreateCaeIndeXVolumeSlice, Eddy_Viscosity mapping, automatic colormap/range inheritanceUse Cases: Consistent volume+slice visualization, automatic colormaps, standard IndeX workflow
Core Examples (omni.cae.kit)
# Geometric analysis
./repo.sh launch -n omni.cae.kit -- --exec scripts/example-bounding-box.py
./repo.sh launch -n omni.cae.kit -- --exec scripts/example-faces.py
./repo.sh launch -n omni.cae.kit -- --exec scripts/example-points.py
./repo.sh launch -n omni.cae.kit -- --exec scripts/example-glyphs.py
# IndeX rendering
./repo.sh launch -n omni.cae.kit -- --exec scripts/example-slice.py
./repo.sh launch -n omni.cae.kit -- --exec scripts/example-volume.py
# NumPy data
./repo.sh launch -n omni.cae.kit -- --exec scripts/example-npz.py
./repo.sh launch -n omni.cae.kit -- --exec scripts/example-npz-point-cloud.py
# Flow/NanoVDB advanced
./repo.sh launch -n omni.cae.kit -- --exec scripts/example-npz-volume-streamlines.py
./repo.sh launch -n omni.cae.kit -- --exec scripts/example-nvdb-slice.py
./repo.sh launch -n omni.cae.kit -- --exec scripts/example-nvdb-slice-on-volume.py
./repo.sh launch -n omni.cae.kit -- --exec scripts/example-slice-on-volume.py
VTK Examples (omni.cae_vtk.kit)
# VTK packages (first time)
mkdir -p pip_archives
./repo.sh pip_download --dest pip_archives -r ./tools/deps/requirements.txt
# Run VTK examples
./repo.sh launch -n omni.cae_vtk.kit -- --/exts/omni.kit.pipapi/archiveDirs=[pip_archives] --exec scripts/example-headsq-vti.py
./repo.sh launch -n omni.cae_vtk.kit -- --/exts/omni.kit.pipapi/archiveDirs=[pip_archives] --exec scripts/example-streamlines.py
Git LFS Issues
Symptom: CGNS file detected as ASCII text
file StaticMixer.cgns
# Wrong: ASCII text
Fix:
sudo apt install git-lfs
git lfs install
git lfs pull
Verify:
file StaticMixer.cgns
# Correct: Hierarchical Data Format (version 5) data
VTK Dependency Issues
Symptom: ModuleNotFoundError: No module named 'vtkmodules'
Fix:
./repo.sh pip_download --dest pip_archives -r ./tools/deps/requirements.txt
./repo.sh launch -n omni.cae_vtk.kit -- --/exts/omni.kit.pipapi/archiveDirs=[pip_archives] --exec scripts/[example].py
Common Runtime Errors
The full set of 14 Kit-CAE examples delivers a complete CAE visualization workflow:
Summary by Category
Geometric Analysis (4)
Advanced Rendering (6)
Data Format Support (4)
Core Tech Stack
Completeness Check
All 14 examples run successfully, confirming Kit-CAE as a comprehensive CAE visualization solution offering:
Share this post: