https://docs.isaacsim.omniverse.nvidia.com/latest/sensors/index.html
Isaac Sim’s sensor system is divided into six categories and supports simulation of various sensors that are physics-based, RTX-based, camera-based, and applicable to real robots. Each category is used for the following purposes.
| Sensor Category | Description | Primary Uses |
|---|---|---|
| Camera Sensors | Simulation of visual sensors such as RGB/Depth | Training data collection, Sim-to-Real, SLAM |
| RTX Sensors | RTX-based lidar/radar sensors | Precise detection of distance, velocity, and reflectance |
| Physics-Based Sensors | Sensors based on the physics engine (IMU, contact, etc.) | Robot motion, force, and collision detection |
| PhysX SDK Sensors | Lightweight sensors based on PhysX SDK raycast | Simple distance sensing, performance optimization |
| Camera and Depth Sensors | Real camera models provided as USD | Digital twins of RealSense, ZED, Orbbec, etc. |
| Non-Visual Sensors | USD assets of physics-based sensors | IMU, proximity, contact, etc. |
https://docs.isaacsim.omniverse.nvidia.com/latest/sensors/isaacsim_sensors_camera.html
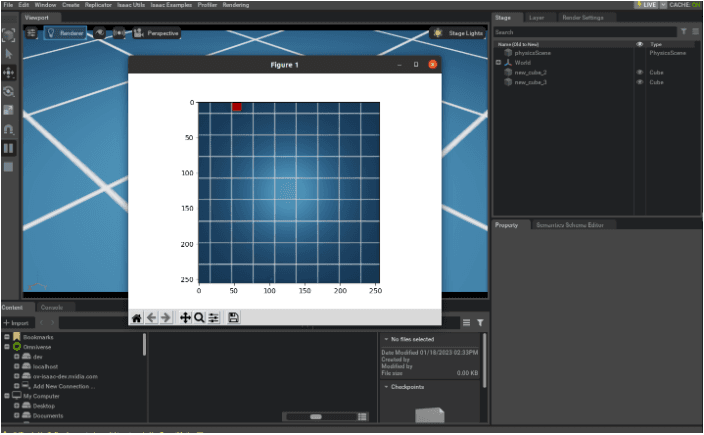
The basic RGB/Depth cameras used in Isaac Sim can be simulated similar to real lenses and support various annotator outputs.
What are Annotators?
In Isaac Sim, an annotator automatically generates additional ground-truth data streams beyond the images produced by a sensor.
This data is extremely useful for machine learning training, robot perception, and validation.
Major Annotator Types and Descriptions:
| Annotator | Description | Example Uses |
|---|---|---|
| RGB | Standard color image | Image classification, recognition |
| Depth | Per-pixel distance map | Range perception, SLAM |
| Normals | Surface normal vectors | Pose estimation, material analysis |
| Motion Vectors | Inter-frame motion vectors | Object tracking, motion blur |
| Instance ID | Unique ID per object | Instance segmentation |
| Semantic ID | Class ID (e.g., person=1, box=2) | Semantic segmentation |
| 2D/3D BBox | Automatic bounding boxes | Object detection |
| Optical Flow | Per-pixel velocity vectors | Robot vision, autonomous driving prediction |
In Isaac Sim, this data can be output as .png, .json, .npy, ROS messages, etc., and can be controlled via Python API or Action Graph.
Supported Features:
Example Uses:
https://docs.isaacsim.omniverse.nvidia.com/latest/sensors/isaacsim_sensors_rtx.html
A family of high-precision sensors for distance/velocity detection using NVIDIA RTX acceleration. It consists of lidar, radar, and visual annotators.
Subcomponents:


Example Uses:
Visual Materials (Sensor Materials for Visual Response)
Simulate the visual properties of object surfaces that RTX sensors detect (e.g., reflectance, absorption).
These affect both rendering and sensor response; a total of 21 fixed material types are provided.
| Index | Material Type | Description (Expected) |
|---|---|---|
| 0 | Default | Default material |
| 1 | AsphaltStandard | Standard asphalt road |
| 2 | AsphaltWeathered | Weathered asphalt |
| 3 | VegetationGrass | Grass/vegetation |
| 4 | WaterStandard | Water surface |
| 5 | GlassStandard | Standard glass |
| 6 | FiberGlass | Fiberglass |
| 7 | MetalAlloy | Alloy metal |
| 8 | MetalAluminum | Aluminum |
| 9 | MetalAluminumOxidized | Oxidized aluminum |
| 10 | PlasticStandard | Standard plastic |
| 11 | RetroMarkings | High-reflective road markings |
| 12 | RetroSign | High-reflective traffic sign |
| 13 | RubberStandard | Rubber |
| 14 | SoilClay | Clay soil |
| 15 | ConcreteRough | Rough concrete |
| 16 | ConcreteSmooth | Smooth concrete |
| 17 | OakTreeBark | Oak tree bark |
| 18 | FabricStandard | Fabric |
| 19 | PlexiGlassStandard | Plexiglass |
| 20 | MetalSilver | Silver metal |
| 31 | INVALID | Invalid (for exception handling) |
Non-Visual Sensor Material Properties
Do not affect rendering, but control detectability and reflectance strength for RTX sensors.
This allows specific objects to be detected or ignored in simulation.
Purposes:
| Property Name | Type | Description |
|---|---|---|
| no_sensor_hit | bool | If True, not detected by RTX sensors (sensor-transparent) |
| sensor_visibility_boost | float | Default 1.0; higher values make it more detectable (simulate strong reflection) |
https://docs.isaacsim.omniverse.nvidia.com/latest/sensors/isaacsim_sensors_physics.html
Sensors implemented based on interactions in the physics engine (PhysX) to sense internal robot states or external contacts.
Supported Sensors:
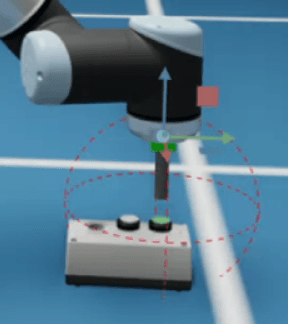
Example Uses:
https://docs.isaacsim.omniverse.nvidia.com/latest/sensors/isaacsim_sensors_physx.html
Lightweight distance sensors using the PhysX SDK’s raycast functionality.
Supported Items:
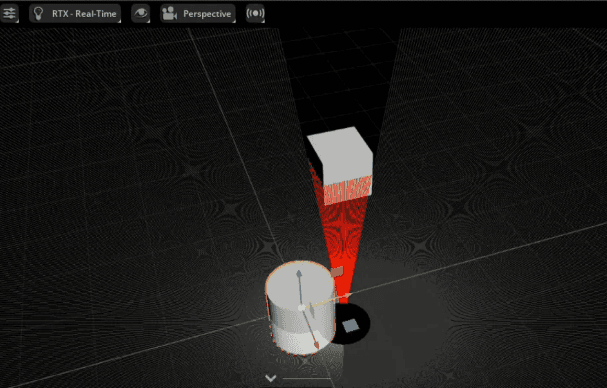
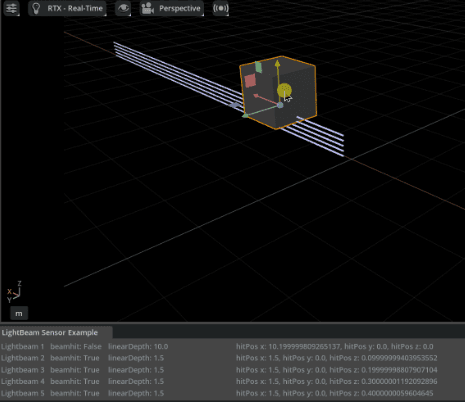
Example Uses:
https://docs.isaacsim.omniverse.nvidia.com/latest/assets/usd_assets_camera_depth_sensors.html
A collection of USD-based camera and depth sensor assets modeled after frequently used real sensors.
Included Sensors:

| Manufacturer | Model (Product Name) | Type |
|---|---|---|
| Leopard Imaging | Hawk Stereo Camera (LI-AR0234CS-STEREO-GMSL2-30) | Stereo RGB + IMU |
| Owl Fisheye Camera (LI-AR0234CS-GMSL2-OWL) | Fisheye RGB Camera | |
| Sensing | SG2-AR0233C-5200-G2A-H100F1A | HDR mono camera |
| SG2-OX03CC-5200-GMSL2-H60YA | HDR camera for ADAS | |
| SG3-ISX031C-GMSL2F-H190XA | 3MP automotive camera | |
| SG5-IMX490C-5300-GMSL2-H110SA | 5MP ADAS + surround view | |
| SG8S-AR0820C-5300-G2A-H30YA | 4K HDR automotive camera | |
| SG8S-AR0820C-5300-G2A-H60SA | 4K HDR automotive camera | |
| SG8S-AR0820C-5300-G2A-H120YA | 4K HDR automotive camera | |
| Intel | RealSense D455 | RGB + Depth + IMU |
| Orbbec | Gemini 2 | Depth via active stereo IR |
| Femto Mega | RGB + multi-mode depth | |
| Gemini 335 | Depth | |
| Gemini 335L | Depth | |
| Stereolabs | ZED X | Stereo RGB + IMU |
Example Uses:
https://docs.isaacsim.omniverse.nvidia.com/latest/assets/usd_assets_nonvisual_sensors.html
A collection of assets for digital twins of non-visual sensors (IMU, force, contact, etc.).
Asset Contents:
| Manufacturer | Model | Sensor Type | Notes |
|---|---|---|---|
| NVIDIA | Debug Rotary | Rotary lidar (for debugging) | No mesh |
| Example Rotary 2D | 2D rotary lidar | No mesh | |
| Example Rotary | 3D rotary lidar | No mesh | |
| Example Solid State | Solid-state lidar | No mesh | |
| Simple Example Solid State | Simple solid-state lidar | No mesh | |
| HESAI | XT32 SD10 | 32-channel 360° spinning lidar | Certified |
| Ouster | OS0 | High-res 3D lidar (short-range) | Multiple configs |
| OS1 | High-res 3D lidar (mid-range) | Multiple configs | |
| OS2 | High-res 3D lidar (long-range) | Multiple configs | |
| VLS 128 | Ultra high-res long-range lidar | ||
| SICK | microScan3 | 2D safety lidar | Certified |
| multiScan136 | 3D lidar | Certified | |
| multiScan165 | 3D lidar | Certified | |
| nanoScan3 | Ultra-compact safety lidar | Certified | |
| picoScan150 | 2D industrial lidar | Certified | |
| TiM781 | 2D collision/monitoring lidar | Certified | |
| SLAMTEC | RPLIDAR S2E | 2D scanning lidar | Low-cost |
| ZVISION | ML-30s+ | Short-range solid-state automotive lidar | Certified / no mesh |
| ML-Xs | Long-range solid-state automotive lidar | Certified / no mesh |
Example Uses:
Share this post: